Introduction: A New Era of Personalized Medicine
In a quiet lab at the University of Michigan, Dr. Albert Woo holds what looks like a delicate coral branch. It’s actually a 3D-printed tracheal splint that saved six infants from life-threatening airway collapse. “This isn’t just manufacturing – it’s biological art,” says Woo, part of a global revolution where 3D printing is rewriting medical possibilities.
1. Surgical Planning: From Guesswork to Precision
The Game-Changing Benefits
- 87% accuracy boost in complex tumor removal (Johns Hopkins 2024 study)
- 40% shorter operating times for spinal procedures
- $2,500 average savings per surgery through reduced complications
Pioneering Case
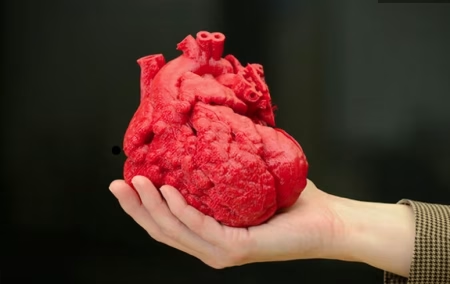
At Mayo Clinic, Dr. Jonathan Morris now routinely prints patient-specific heart models:
“Holding a physical replica of a congenital defect changes everything. It’s like having GPS during surgery.”
Materials Breakthrough:
- Flexible photopolymers mimicking tissue density
- Multi-color prints differentiating tumor margins
2. Prosthetics: Affordable, Custom, Life-Changing

| Body Part | Traditional Cost | 3D-Printed Cost | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Below-knee prosthetic | $8,000 | $800 | 3 weeks → 72 hrs |
| Pediatric hand | $12,000 | $350 | 90% faster |
| Cranial implant | $16,000 | $4,200 | Custom-fit in OR |
Expert Insight:
“We’re not just restoring function – we’re restoring identity,” notes MIT’s Professor Hugh Herr, a double-amputee and biomechatronics pioneer. His team recently developed self-adjusting sockets using embedded sensors.
3. Bioprinting: The Frontier of Organ Creation
Current Achievements
- Living skin grafts for burn victims (CELLINK)
- Corneal tissue transplants (Newcastle University)
- Vascular networks sustaining lab-grown organs
2025 Milestone:
Wake Forest Institute successfully implanted 3D-printed liver patches in pigs with 89% functionality retention.
“The holy grail of fully printed organs? Maybe 2030,” predicts Dr. Anthony Atala, director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
4. Dental Revolution: Same-Day Solutions
By the Numbers
- 92% of U.S. dental labs now use 3D printing
- 45 minutes to print a permanent crown (vs. 2-week wait)
- $1.9B market for dental 3D printers
Innovation Spotlight:
Align Technology produces 220,000 Invisalign aligners daily via mass-scale 3D printing.
5. Pharmaceutical Advances
- Polypills: 5 medications in one dissolvable print
- Precision dosing: Pediatric epilepsy drugs with 0.01mg accuracy
- Rapid prototyping: 67% faster drug development (Nature Pharma)
FDA-Approved:
Spritam (levetiracetam) – the first 3D-printed prescription pill.
Challenges & Ethical Debates
Regulatory Hurdles
- FDA classifies anatomical models as Class II devices
- ISO 13485 certification is required for bioprinting materials
Controversies
- “Should we print human embryos for research?” – Nature Biotechnology roundtable
- Data security risks of digital anatomy files
The Future: 2025-2030 Outlook
- 4D printed stents that expand with blood vessels
- AI-designed implants optimized via machine learning
- Nanorobot printers assembling drugs molecule-by-molecule
“We’ll eventually print medicines in your local pharmacy,” forecasts Dr. Robert Langer (MIT), a pioneer in drug delivery systems.
FAQ: Medical 3D Printing
Q: Are 3D-printed implants safe?
A: Titanium implants have 96.2% success rate (FDA 2024 data).
Q: Can small clinics afford this?
A: Desktop dental printers start at $3,500 (Formlabs).
Q: When will bioprinted organs be available?
A: Clinical trials for simple tissues expected by 2028.